Introduction
Welcome to our complete exploration of the working principle of infrared sensors, where we'll look into the complexities of their functionality and multiple uses.
Infrared (IR) sensors are electrical components that detect particular waves of radiation, including heat. Infrared sensors enable systems to detect their surroundings and respond appropriately.
The working of IR sensor involves detecting infrared waves emitted from a person or object that enter the sensing area of the device containing an Infrared (IR) sensor.
This information is then processed and used for various functions such as identifying objects in proximity to it, determining whether something is moving around itas surroundings or even steering robots towards a target location via detection distance measurement data provided by the infrared signal detected at each point along its trajectory path within range of sight.
Along with this basic functionality, modern-day applications include home security systems which use motion detectors combined with cameras triggered upon receiving specific signals from these small yet significant pieces of technology making them essential elements in robotics projects today!
What is IR Sensor
Understanding the working principle of IR sensors is akin to comprehending object detection sensors. Let's demystify the magic behind these sensors.

In our daily lives, Infrared technology plays a crucial role. For instance, TVs utilize an IR sensor to decode signals from remote controls. Let's delve deeper into the working principle of IR sensors and their significance.
Infrared technology is used in everyday life as well as in industry for a variety of purposes. TVs, for example, infrared sensor used to decode the signals transmitted by remote control.
The main advantages of IR sensors are their low power consumption, simple design, and useful features. IR signals are undetectable to the human eye. In the electromagnetic spectrum, IR radiation can be found in the visible and microwave regions.

The wavelengths of these waves typically range from 0.7µm to 5 to 1000 µm. Near-infrared, mid-infrared, and far-infrared are the three regions of the IR spectrum. The wavelength ranges from 0.75 to 3 µm in the near-infrared region, 3 to 6 µm in the mid-infrared region, and more than 6 µm in the far IR region.
An infrared sensor is a device that detects infrared radiation in its environment and outputs an electric signal. this sensor can detect movement as well as to measure the heat of an object.
This sensor can detect infrared radiation, which is invisible to our eyes. This sensor is a photodiode that is sensitive to infrared light. When infrared light hits the photodiode, the resistances and output voltages change in proportion to the magnitude of the IR light.
Infrared (IR) sensors are used to detect and measure the presence of an object within a given area. They can be found in many applications, from industrial robots to home security systems. these sensors operate by measuring differences in infrared radiation emitted or reflected off objects relative to their surrounding environment.
The sensor then analyzes these changes so as determine if any particular object is present within its field of view – this information can provide valuable data for making necessary automated decisions based on predetermined conditions.
As such, they’re becoming increasingly popular in automation projects with widely varying output requirements that extend far beyond just detecting movement and obstacles along production lines; like temperature regulation inside large buildings or warehouses, for instance!
With ever-improving technologies at our disposal today, it looks like we'll only see further development ahead when it comes to incorporating IR sensors into different types of commercial products regardless of industry type!
Infrared Sensor Working

The IR sensor working as similarly to the object detection sensor. The working of IR sensor totally depends on whether the sensor is active or passive (PIR).
Active infrared sensors emit and receive infrared radiation, detecting movement and distance.
Passive infrared sensors, like PIR sensors, only receive radiation emitted by nearby objects. PIR sensors are mostly used in physical security.
Consider installing a home security system. You choose to use both active and passive infrared sensors to ensure that all corners are covered. So you deploy active infrared sensors along the perimeter of your property.
These sensors emit invisible infrared light beams. When something crosses the course of these beams, the sensor detects an interruption and sounds an alarm. This is good for detecting movement and alerting you to prospective attackers.
Place the passive infrared sensors in strategic areas near entry points like doors and windows. PIR sensors, unlike active sensors, do not emit radiation. They can detect infrared light from heated objects from their perspective.
So, when a person walks through a PIR sensor, their body heat releases infrared radiation, which the sensor recognizes and activates the alert.
This example will help you understand how IR sensors work in security systems and we will go over the various types of infrared sensors in greater detail later.
This sensor uses physics laws such as Plank's radiation, Stephan Boltzmann, and Wein's displacement.
- Planck's Radiation Law: According to this law anything with a temperature over absolute zero (0 Kelvin) emits radiation.
- Stephan Boltzmann's Law: According to this law the total energy produced by a black substance across all wavelengths is appropriate to its absolute temperature.
- Wein’s Displacement Law: Objects of different temperatures emit spectra that peak at different wavelengths that are inversely proportional to Temperature.
How does an IR sensor work
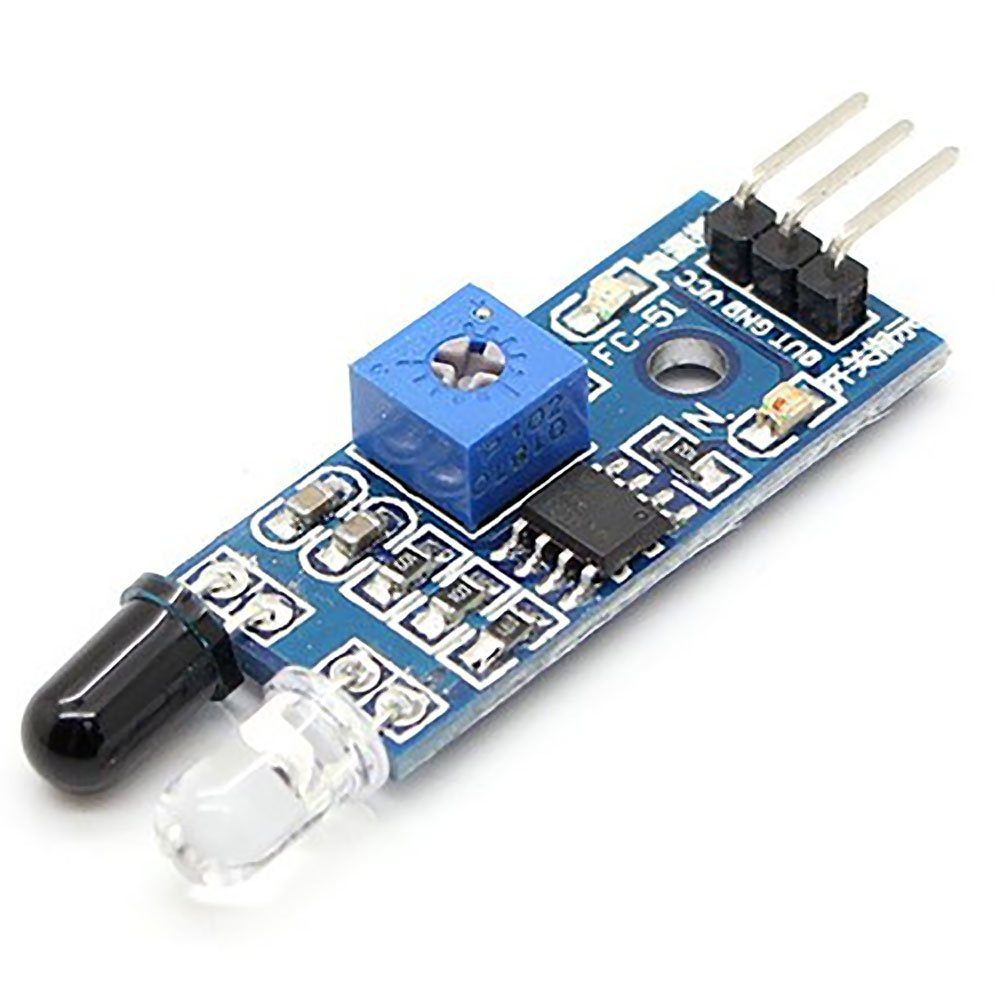
This sensor includes an IR LED & an IR Photodiode, so combining these two can be formed as a photo-coupler otherwise optocoupler.
IR Transmitter or IR LED
IR LED is one kind of transmitter that emits IR radiation. This LED has the appearance of a standard LED, and the radiation it emits is not visible to the human eye.
An infrared transmitter is used to detect the radiation by infrared receivers.

IR Receiver or Photodiode
Infrared receivers are available in photodiode form. IR Photodiodes are different from regular photodiodes in that they only detect IR radiation.
Different types of infrared receivers exist based on voltage, wavelength, package, and other factors.

When used as an IR transmitter and receiver, the wavelength of the receiver must match that of the transmitter. The transmitter is an infrared LED, and the receiver is an infrared photodiode.
The infrared photodiode is activated by the infrared light produced by an infrared LED. The photodiode's resistance and the change in output voltage are proportional to the amount of infrared light obtained.
This is the fundamental IR sensor working principle.
Once the infrared transmitter generates emission, when it arrives at the object & some of the emission will reflect toward the infrared receiver.
The sensor output can be decided by the IR receiver depending on the intensity of the response.
IR Proximity Sensor Working Principle

The working principle of the IR Proximity sensor is the same as the working principle of the IR sensor as explained above. Infrared light (IR) is based on the principles of optics.
An IR proximity sensor works by applying a voltage to a pair of IR light-emitting diodes (LEDs) which in turn, emit infrared light.
This light propagates through the air and once it hits an object it is reflected towards the sensor. If the object is close, the reflected light will be stronger than if the object is further away.
Also, read our blog Proximity Sensor Types detailing 5 types of proximity sensors and their working principles.
Types of IR Sensors
1. Active IR Sensor

This type of sensor includes both the emitter & the receiver which are also known as transmitter & receiver. In the majority of cases, a laser diode or LED is used as a light source.
LEDs are used for non-imaging infrared sensors, while laser diodes are used for imaging infrared sensors.
This sensor works by emitting energy that is detected and received by the detector.
To obtain the required data, it is further processed through a signal processor. Reflectance and break beam sensors are the best examples of active infrared sensors.
2. Passive IR Sensor

The passive infrared sensor includes detectors only but they don’t include a transmitter. These sensors make use of a transmitter or an infrared source.
This object emits energy, which infrared receivers detect. After that, a signal processor is used to decode the signal and extract the necessary data.

The best examples of this sensor are pyroelectric detector, bolometer, thermocouple-thermopile, etc. These sensors are classified into two types thermal IR sensors and quantum IR sensors.
- Thermal Infrared Sensor

These types of sensors are independent of wavelength and they utilize heat-like energy sources. These are slow along with the response time as well as detection time.
- Quantum Infrared Sensor

These types of sensors depend on wavelengths and the response time and they have high detection. These kinds of sensors need repeated cooling for exact measurement.
Advantages of IR sensor
- These sensors are inexpensive and simple to integrate into current systems, which makes them an excellent choice for enterprises of any size.
- These sensors offer a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to home security. These can be used for both short as well as long-range sensing.
- Responses tend to be very fast when using infrared due to its high-frequency waves that travel quickly over large distances in the air without having any obstacles or refraction interference along the way.
- It is not affected by wind pressure changes which makes it suitable for motion detection indoors or outdoors under varying conditions such as rain and snowfall days unlike other types of sensor technology available on the market today.
- When compared with ultrasonic technologies, there’s considerably less power consumption associated with infrared providing longer battery life across mobile platforms such as autonomous robots & drones powered by batteries alone..
- Due to their small form factor and low profile design instructions they require minimal space allowing even tight spaces like elevator shafts within buildings where no other solution may work - this has made InfraRed an ideal choice for many consumer electronics companies who must adhere to strict dimensional requirements during product development cycles these days too!
- Furthermore using light signals rather than sound means these devices do not transmit noise pollution eliminating possible interferences between different electronic components/appliances nearby ensuring data accuracy while saving energy at the same time!
Disadvantages of IR sensor
- Infrared(IR) sensors are prone to interference from heat sources such as direct sunlight or high-powered lamps, which can cause readings to be inaccurate or unreliable.
- The IR sensor has a limited signal range and can fail to deliver an accurate reading over long distances or through walls or other obstacles that might block the signal route between the system's transmitter and receiver elements.
- High humidity levels in the surroundings where these sensors work may also cause problems with their operation, which might result in false-positive readings even when no actual motion occurs within the viewable distance limits of this sort of device.
- Reliability issues due to rapid ageing if subjected to constantly changing temperatures affecting how well they track movement over time could lead to less than satisfactory results during use in outdoor locations exposed directly to extreme temperature fluctuation conditions like climates being close to Sea/Ocean surroundings.
Applications of IR Sensors
IR sensors have found their applications in most of today’s equipment. Following is the list of sensors that are named after their usage. It helps you to understand what is IR sensor used for.
1. Proximity Sensor: These are used in cellphones to measure the distance between objects. These are used in mobile phones to determine the distance between two objects. They use a principle called Reflective Indirect Incidence.
The receiver receives radiation broadcast by the transmitter after it has been reflected by an object. Distance is calculated using the intensity of the radiation received.
2. Item Counter: This uses the direct incidence approach to count the items. The transmitter and receiver maintain a consistent radiation level.
As soon as the object cuts the radiation, the item is detected and the count is increased. The same count is shown on a display system.
3. Burglar Alarm: This is one of the widely and commonly used sensor applications. It is another example of the direct incidence method.
It works similar to the item counter, where the transmitter and receiver are kept on both sides of a door frame. Constant radiation is maintained between transmitter and receiver, whenever an object crosses the path alarm starts.
4. Radiation Thermometers: It is one of the key Infrared sensor applications. The working of a radiation thermometer depends on temperature and type of object.
These have faster response and easy pattern measurements. They can do measurements without direct contact with an object.
5. Human Body Detection: This method is used in intrusion detection, auto light switches, etc. An intrusion alarm system senses the temperature of the human body.
If the temperature is more than the threshold value, it sets the alarms. It uses an electromagnetic system that is suitable for the human body to protect it from unwanted harmful radiation.
6. Gas Analyzers: Gas analyzers use infrared absorption properties to assess gas density. There are dispersive and non-dispersive gas analyzers available.
7. Other applications: These sensors are also used in infrared imaging, optical power meters, sorting machines, missile guidance, remote sensing, flame monitors, moisture analyzers, and night vision.
Conclusion
Finally, we explored into the intriguing world of infrared sensor operating principles and their applications in a variety of technical fields of study.
These sensors use infrared light to detect objects, calculate distances, and even identify materials. These sensors are used in a variety of fields, including automation, robotics, medical, and aerospace. They can range from simple proximity sensors to complicated thermal imaging systems.
So, if you're seeking for a dependable, adaptable, and effective way to perceive your environment, consider implementing an IR sensor into your next project.
If you understand what is IR sensor and how it works and appreciate our work don't forget to share this post and leave your opinion in the comment box.
Please do check out other blog posts about Popular electronics
Check out other related blog posts PIR Sensor Working Principle , IR Sensor Interfacing with Arduino and DIY IR SENSOR
Make sure you check out our wide range of products and collections (we offer some exciting deals!)